
Half Man, Half Machine: Becoming Robotic
What’s in the Story?

Darth Vader, Luke Skywalker, Dr. Octopus, or Master Chief—what do they all have in common? Besides being famous villains and heroes, they are all part robot, or cyborgs.
Have you wondered if it were possible to become part robot like any of these characters? Thanks to science, it is no longer impossible. The PLOS Biology journal article “Learning to Control A Brain-Machine Interface for Reaching and Grasping by Primates,” discusses how our brains can control robotic parts.
Becoming a Machine
A great example of this comes from the movie Spider-Man 2. Dr. Octopus is a scientist who invents four mechanical, octopus-like arms. He attaches them to his back so he can control them from his spinal cord. Then “Doc Oc” controls his robot arms with his own thoughts! Of course, things go wrong and the machine arms start to control him, making him a villain that Spider-man must stop.
Modern day science has not advanced to the point where you can have giant robot arms attached to your back, but we do know it's not completely impossible. Some researchers are finding which parts of the central nervous system work best to control robot arms. When they find a good area, they attach a Brain-Machine Interface to connect the robotic parts to the nervous system. Scientists are already finding out what part of the brain works best to control robot parts.
Getting in Your Head
In the Dr. Octopus example, he thought that the best place for a brain-machine interface was in his spinal column because there are lots of neurons in the spinal cord. Neurons are the cells that receive and send signals between the brain and the muscles. But researchers in this study were more interested in how brain-machine interfaces connect to the brain, which also has lots of neurons. The scientists knew certain spots in the front and sides of the brain work better than others for this kind of task.
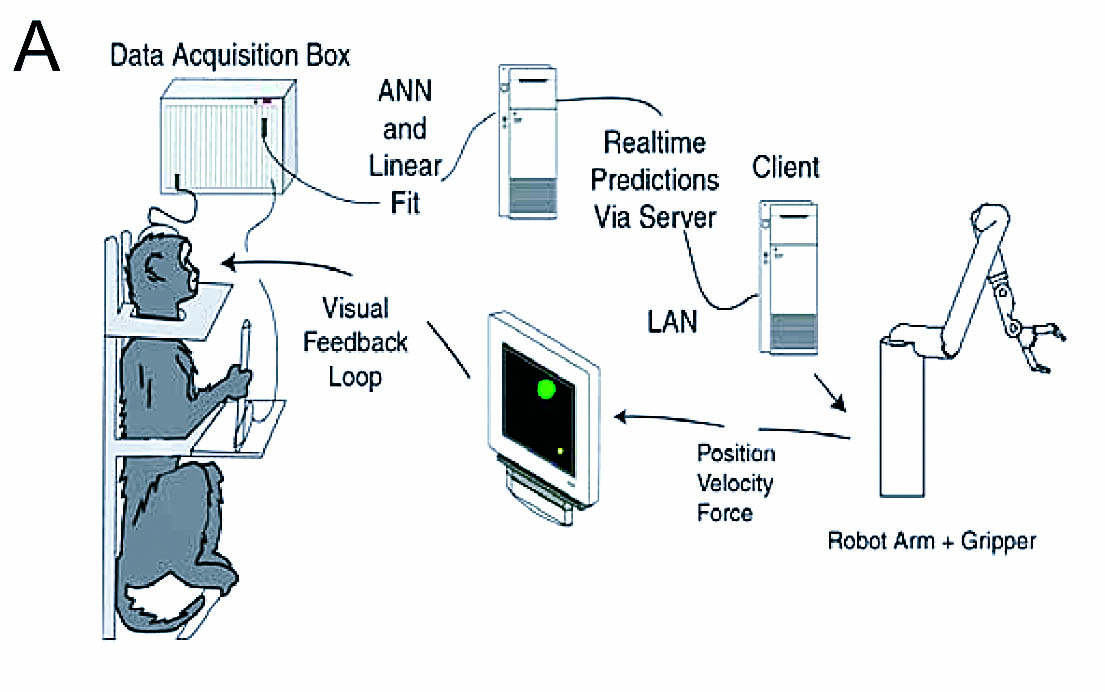
In the experiment, monkeys were trained to use a control stick and move it with their arms. This is kind of like using an old video game controller. The monkeys used these control sticks to move one ball on a screen to a specific place on the other side of the screen. Once the monkeys got the hang of it, the control stick was removed and they watched the ball being moved on its own. The trick was that the monkeys still thought they were controlling the motion. Finally, a robot arm was placed near the monkeys to make the same moves. Scientists took all of these steps so that the monkeys thought they were in control of the robotic arm moving the ball.
During all of these steps, the scientists watched the brain wave patterns from the monkeys to see how different parts of the brain acted. The researchers monitored four specific areas of the brain to record how the monkeys thought when they were moving the control stick, versus "moving" the robotic arm. This information was then used to recommend the best places to put a brain-machine interface.
What Did They Find?
After using many graphs and doing a lot of math, the team found that the front and sides of the brain contain lots of neurons that send signals to make your muscles move. Scientists suggested that any place in the brain was suitable to attach a brain-machine interface, as long as it was attached to plenty of neurons. They also found out that it takes time to learn how to use the brain-machine interface. Scientists saw that the monkeys slowly adjusted to the robot arm, but with practice they thought their brains were using it.
What does this mean for us? It means that like Dr. Octopus, maybe people can start to use robotic limbs better. Scientists think that by using the areas they found, a brain-machine interface can work better in humans. Not only that, but scientists have shown that if you use a brain-machine interface like a robotic arm often enough, it would become easier to use and might even feel like it is an actual part of the body. Just look at this guy playing checkers with his robotic arm!

Robot drawing from Wikimedia - Mikael Nordin
Hand with robot hand from Wikimdia - Richard Greenhill and Marie De Ryck
Robot hand and light bulb from Wikimedia - Richard Greenhill and Hugo Elias
Bibliographic details:
- Article: Half Man, Half Machine: Becoming Robotic
- Author(s): Daniel Maas
- Publisher: Arizona State University School of Life Sciences Ask A Biologist
- Site name: ASU - Ask A Biologist
- Date published: 31 Oct, 2011
- Date accessed: 3 September, 2025
- Link: https://askabiologist.asu.edu/plosable/half-man-half-machine-becoming-robotic
APA Style
Daniel Maas. (Mon, 10/31/2011 - 20:34). Half Man, Half Machine: Becoming Robotic. ASU - Ask A Biologist. Retrieved from https://askabiologist.asu.edu/plosable/half-man-half-machine-becoming-robotic
Chicago Manual of Style
Daniel Maas. "Half Man, Half Machine: Becoming Robotic". ASU - Ask A Biologist. 31 Oct 2011. https://askabiologist.asu.edu/plosable/half-man-half-machine-becoming-robotic
MLA 2017 Style
Daniel Maas. "Half Man, Half Machine: Becoming Robotic". ASU - Ask A Biologist. 31 Oct 2011. ASU - Ask A Biologist, Web. https://askabiologist.asu.edu/plosable/half-man-half-machine-becoming-robotic

Be Part of
Ask A Biologist
By volunteering, or simply sending us feedback on the site. Scientists, teachers, writers, illustrators, and translators are all important to the program. If you are interested in helping with the website we have a Volunteers page to get the process started.



