How Do You Know If an Animal Can See Color?
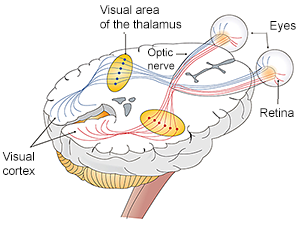
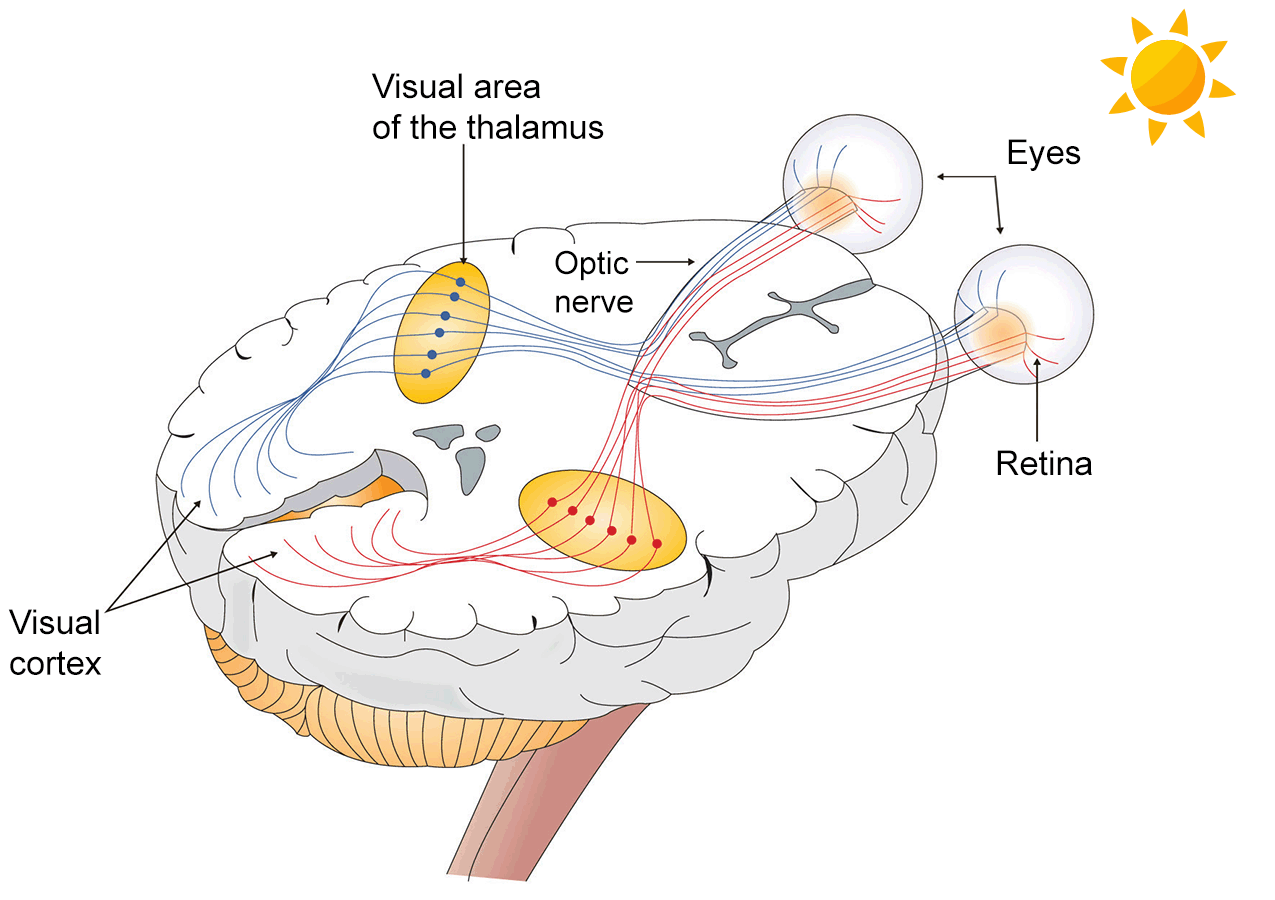
This question can be answered pretty easily. If an animal eye has cones they will be able to see some color. What is difficult to know is which colors an animal can see and how strong or weak the color will appear to the animal.
Scientists can study an animal eye and find out if it contains cones and what colors of light the cones can detect. It is also possible to count the number of cones and their location in the retina to understand how strong or weak a color might appear to an animal.
But, what color does the animal see? Vision, like all of our senses, is processed in the brain. Without being able to get into the head of an animal, it is only possible to know what colors can be detected and not how they "look" to the animal.
This is also true for a more familiar animal: the human. Two people may say they see a painted wall as a particular color, but do they see it the same way? The answer is not known at this point.

Do Humans Have Better Color Vision Than Animals?
It is true that we see more colors than some animals. Your pet dog and cat sees fewer and weaker colors. Their view of the world is made of pastel colors. However, some animals see colors we cannot. Spiders and many insects can see a type of light called ultraviolet that most humans cannot see. Other animals, like snakes, are able to see infrared light. You can use the chart below to explore what colors certain animals see and how they compare to human color vision.
COMMON ANIMALS AND THE COLORS THEY CAN SEE
| ANIMAL | THE COLORS THEY SEE | RELATIVE TO HUMANS |
| SPIDERS (jumping spiders) | ULTRAVIOLET AND GREEN | Different |
| INSECTS (bees) | ULTRAVIOLET, BLUE, YELLOW | Different |
| CRUSTACEANS (crayfish) | BLUE AND RED | Less |
| CEPHALOPODS (octopi and squids) | BLUE ONLY | Less |
| FISH | MOST SEE JUST TWO COLORS | Less |
| AMPHIBIANS (frogs) | MOST SEE SOME COLOR | Less |
| REPTILES (snakes*) | SOME COLOR AND INFRARED | Different |
| BIRDS | FIVE TO SEVEN COLORS | More |
| MAMMALS (cats) | TWO COLORS BUT WEAKLY | Less |
| MAMMALS (dogs) | TWO COLORS BUT WEAKLY | Less |
| MAMMALS (rabbit) | BLUE AND GREEN | Less |
| MAMMALS (rats) | ULTRAVIOLET, BLUE, GREEN | Different |
| MAMMALS (squirrels) | BLUES AND YELLOWS | Less |
| MAMMALS (primates-apes and chimps) | SAME AS HUMANS | Same |
| MAMMALS (African monkeys) | SAME AS HUMANS | Same |
| MAMMALS (South American monkeys) | CAN'T SEE RED WELL | Less |
| * pit vipers, some boas and some pythons |
How Do Some Animals See Colors Differently Than Humans?
Below are two examples of how humans see the world compared to how some other animals are likely to see it. One is a butterfly that can see in the ultraviolet wavelength and the other is a rattle snake that can see in the infrared wavelength.

Humans see the world differently than most other animals. We have three types of cones that detect different colors in what are called the visible light waves. Here we see how a person with normal color vision sees a butterfly.

Butterflies can see light that humans cannot see. They see in the ultraviolet wavelength. The vision of butterflies is also not as good as humans. So they do not see things as sharp and detailed.
Many people also think that insects see in kaleidoscope vision, with hundreds of images of the same thing. But that isn't true. Learn more with our story on bug vision.

Humans see light that enters directly into the eye, or is reflected off a surface of an object and then enters the eye. We see the man on the right with his left arm hidden in a black bag. Some animals can see in the infrared wavelengths. A lot of the heat released by objects in the natural environment is infrared. Essentially this means some animals can see heat in a way that humans cannot.
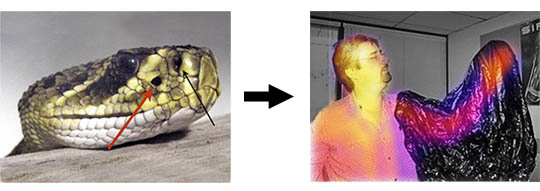
Because rattlesnakes can see in the infrared wavelength, they can see heat. In the picture of the man, his right arm is visible through the bag because it emits heat. Some pythons and boas can also sense heat in this way. On the snake's head, the red arrow points to the pit organs the rattlesnake uses for thermal sensing. Because these snakes have both eyes and pit organs, it is thought that they see a combined image of visual and heat information.
The black arrow in the snake image points to the nostril. Though snakes have a great sense of smell, they don't really use their nostrils to smell. Instead, they smell by picking up chemicals with a flick of the tongue, and transferring those chemicals to a sensory organ at the roof of the mouth.
Images:
Eye, optic nerve, brain illustration from Beginning Psychology (v. 1.0) via Creative Commons (by-nc-sa 3.0). Labels modified for this page.
Additional images via Wikimedia Commons
References:
Gerald H. Jacobs*, John A. Fenwick and Gary A. Williams. (2001, April 19) Cone-based vision of rats for ultraviolet and visible lights. The Journal of Experimental Biology. Retrieved March 14, 2015 from https://jeb.biologists.org/content/204/14/2439.full.
Richard C. Goris. (2011, March) Infrared organs of snakes: An integral part of vision. Journal of Herpetology. Retrieved March 17. 2015 from https://bioone.org/journals/journal-of-herpetology/volume-45/issue-1/10-....
Read more about: Seeing Color
Bibliographic details:
- Article: Colors Animals See
- Author(s): Dr. Biology
- Publisher: Arizona State University School of Life Sciences Ask A Biologist
- Site name: ASU - Ask A Biologist
- Date published: 17 Dec, 2009
- Date accessed: 8 August, 2025
- Link: https://askabiologist.asu.edu/colors-animals-see
APA Style
Dr. Biology. (Thu, 12/17/2009 - 12:37). Colors Animals See. ASU - Ask A Biologist. Retrieved from https://askabiologist.asu.edu/colors-animals-see
Chicago Manual of Style
Dr. Biology. "Colors Animals See". ASU - Ask A Biologist. 17 Dec 2009. https://askabiologist.asu.edu/colors-animals-see
MLA 2017 Style
Dr. Biology. "Colors Animals See". ASU - Ask A Biologist. 17 Dec 2009. ASU - Ask A Biologist, Web. https://askabiologist.asu.edu/colors-animals-see

When comparing the vision of humans and other animals, some animals can see more colors and others see less.
Be Part of
Ask A Biologist
By volunteering, or simply sending us feedback on the site. Scientists, teachers, writers, illustrators, and translators are all important to the program. If you are interested in helping with the website we have a Volunteers page to get the process started.