Do All Cells Look the Same?
Cells come in many shapes and sizes. Some cells are covered by a cell wall, other are not, some have slimy coats or elongated structures that push and pull them through their environment. Some cells have a thick layer surrounding their cell. This layer is called the capsule and is found in bacteria cells.
In our body there are many different kinds of cells. We are made up of about 200 different types of cells. Our body also has non-living materials such as hair, finger nails, and the hard part of teeth (enamel). All these materials are made up of dead cells or other minerals.
What Are the Parts of the Cell?
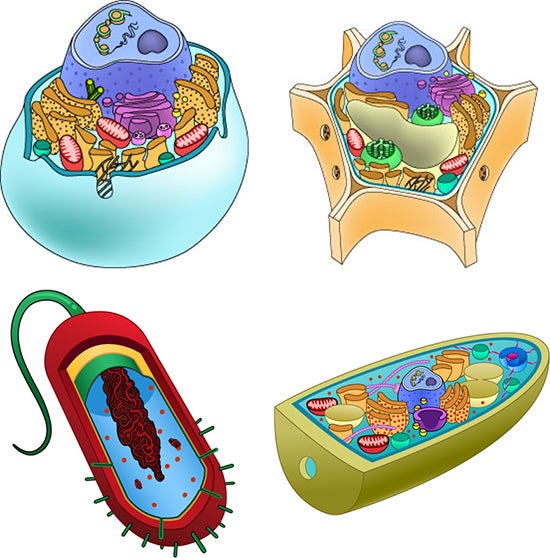
Have you ever wondered what the inside of a cell looks like? If you think about the rooms in our homes, the inside of any animal or plant cell has many similar room-like structures called organelles. Each organelle is a place where specific jobs are done.
Plant and animal cells have many of the same organelles. But in some cases, the organelles in cells are different. For example, in plant cells, there are more types of organelles than are found in animal cells. And fungal cells have organelles not found in any other cell type.
Below are some names and descriptions of organelles commonly found in certain cells. There is also an interactive cell viewer and game that can be used to learn about the parts of animal, plant, fungal, and bacterial cells. Archaea cells are very similar to bacterial cells, so have not been included separately. An introduction video is now available to see how the game is played.
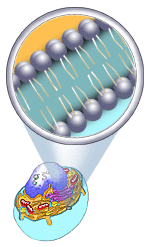 |
Plasma membrane- The membrane enclosing a cell is made up of two lipid layers called a "bilipid" membrane. The lipids that are present in the plasma membrane are called "phospholipids." These lipid layers are made up of a number of fatty acid building blocks. The fatty acid that makes up this membrane has two different parts to it- a small water loving head- hydrophilic head. Hydro stands for water and philic means liking or loving. The other part of this fatty acid is a long water-repelling or water hating tail. This tail is hydrophobic- Hydro stands for water and phobic means fear. The plasma membrane is arranged in such a way so that the tails face each other on the inside and the heads face towards the outside of the membrane. |
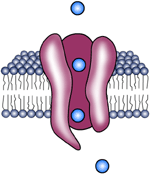 |
Channels/pores- A channel in the cell's plasma membrane. This channel is made up of certain proteins that control the movement of molecules, including food and water, into the cell. |
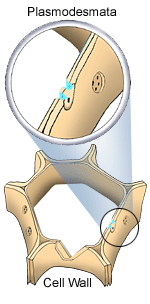 |
Cell wall and plasmodesmata- In addition to cell membranes, plants have cell walls. Cell walls provide protection and support for plants. In land plants, the cell wall is mostly made of cellulose. Unlike cell membranes, materials cannot get through cell walls. This would be a problem for plant cells if not for special openings called plasmodesmata. These openings are used to communicate and transport materials between plant cells because the cell membranes are able to touch and therefore exchange needed materials. |
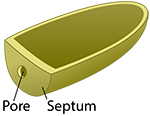 |
Cell wall septum and pores - Fungal cells have both cell membranes and cell walls, like plant cells. Cell walls provide protection and support. Fungal cell walls are largely made of chitin, which is the same substance in insect exoskeletons. Because materials cannot get through cell walls, fungal cells have special openings called pores. Materials can be moved between fungal cells through the pores. Some fungal cells also have a septum (plural is septa) that are special internal walls between cells that are found in long tube-shaped strings or strands called hyphae. |
 |
Cell capsule - Bacterial cells have a cell membrane and a cell wall, but they also have a cell capsule. This outermost layer is often made of sugars or special proteins. It helps protect the bacteria from being eaten by larger cells, like animal immune cells, and from being infected by viruses. back to top |
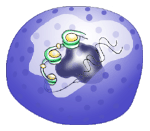 |
Nucleus- The nucleus is the control center of the cell. It is the largest organelle in the cell and it contains the DNA of the cell.

DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) contains all the information for cells to live, perform their functions and reproduce. Inside the nucleus is another organelle called the nucleolus. The nucleolus is responsible for making ribosomes. The circles on the surface of the nucleus are the nuclear pores. These are where ribosomes, and other materials move in and out of the nucleus. |
 |
Nucleoid - Bacteria don't have a nucleus to hold their nuclear DNA. Instead, their DNA is found in the nucleoid. This structure has no protective membrane, but is tightly packed DNA material and also has some RNA and proteins in it. |
 |
Plasmid - In addition to the nucleoid, bacteria have plasmids. Plasmids are small DNA molecules that can hold extra genes that may be used when the cell experiences certain conditions. These little piles of DNA can also be exchanged between bacterial cells. back to top |
 |
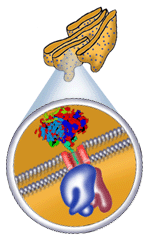
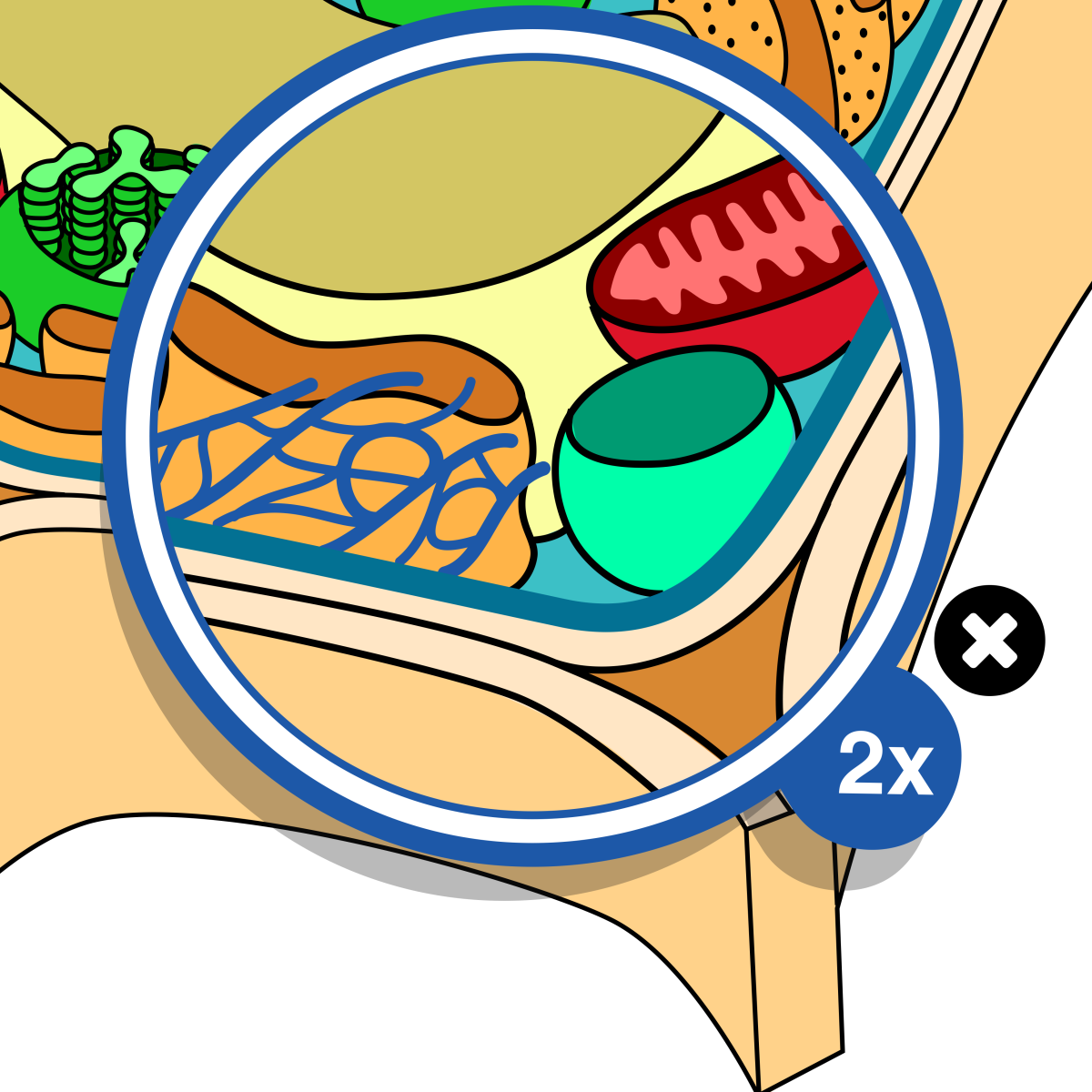
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER)- It is a network of membranes throughout the cytoplasm of the cell. There are two types of ER. When ribosomes are attached it is called rough ER and smooth ER when there are no ribosomes attached. The rough endoplasmic reticulum is where most protein synthesis occurs in the cell. The function of the smooth endoplasmic reticulum is to synthesize lipids in the cell. The smooth ER also helps in the detoxification of harmful substances in the cell. |
|
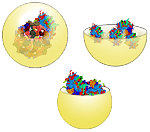
Ribosomes- Organelles that help in the synthesis of proteins. Ribosomes are made up of two parts, called subunits. 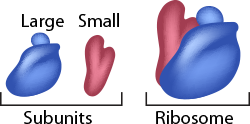
They get their names from their size. One unit is larger than the other so they are called large and small subunits. Both these subunits are necessary for protein synthesis in the cell. When the two units are docked together with a special information unit called messenger RNA, they make proteins. Some ribosomes are found in the cytoplasm, but most are attached to the endoplasmic reticulum. While attached to the ER, ribosomes make proteins that the cell needs and also ones to be exported from the cell for work elsewhere in the body. |
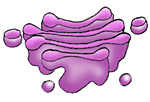 |
Golgi complex- It is the organelle in the cell that is responsible for sorting and correctly shipping the proteins produced in the ER. Just like our postal packages, which should have a correct shipping address, the proteins produced in the ER should be correctly sent to their respective address. It is a very important step in protein synthesis. If the Golgi complex makes a mistake in shipping the proteins to the right address, certain functions in the cell may stop. This organelle was named after an Italian physician, Camillo Golgi. He was the first person to describe this organelle in the cell. It is also the only organelle that is capitalized. |
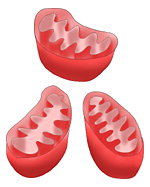 |
Mitochondrion- This is the cell’s powerhouse. This organelle packages the energy from the food you eat into ATP molecules. Every type of cell has a different amount of mitochondria (plural). There are more mitochondria in cells that have to perform lots of work, for example- your leg muscle cells, heart muscle cells etc. Other cells need less energy to do their work and have less mitochondria. |
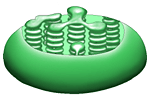 |
Chloroplast- This is the organelle in which photosynthesis takes place. In this organelle the light energy of the sun is converted into chemical energy. Chloroplasts are found only in plant cells not animal cells. The chemical energy that is produced by chloroplasts is finally used to make carbohydrates like starch that get stored in the plant. Chloroplasts contain tiny pigments called chlorophylls. Chlorophylls are responsible for trapping the light energy from the sun. |
 |
Vesicles- This term literally means "small vessel". This organelle helps store and transport products produced by the cell. The vesicles are the transport and delivery vehicles like our mail and Federal Express trucks. Some vesicles deliver materials to parts of the cell and others transport materials outside the cell in a process called exocytosis. |
 |
Peroxisomes- These collect and safely break down chemicals that are toxic to the cell. |
 |
Lysosomes- Created by the Golgi apparatus, these help break down large molecules into smaller pieces that the cell can use. |
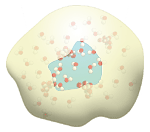 |
Vacuole- Plant cells have what looks like a very large empty space in the middle. This space is called the vacuole. Don't be fooled, the vacuole contains large amounts of water and stores other important materials such as sugars, ions and pigments. |
 |
Centrioles |
 |
Microtubule-organizing center (MTOC) - Fungi have an MTOC that is different from the centrioles found in most animal cells, but it does a similar job. The MTOC builds microtubules that help build an internal cell structure for shape and support. |
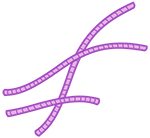 |
Microtubules - Tubular structures that help support cells. Microtubules can be found in any animal, plant, or fungal cell. Part of the cytoskeleton found in animal, plant, and fungal cells. Some bacteria also have microtubules, but not all bacteria. |
 |
Spitzenkörper - The growth center of tube-shaped fungal cells. The Spitzenkörper is made of many small vesicles and dense microfilaments. |
 |
Actin filaments - Long strands of smaller units that play an important role in cell structure. Involved in changing cell shape, in many kinds of cells. Part of the cytoskeleton found in animal, plant, and fungal cells. back to top |
 |
Cytoskeleton- Made up of filaments and tubules, it helps shape and support the cell. It also helps things move around in the cell. For artistic purposes, the cytoskeleton is shown in just one place in the animal cell when in reality it is found throughout the entire cell. back to top |
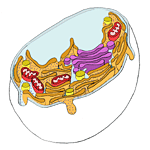 |
Cytoplasm- A term for all the contents of a cell other than the nucleus. Even though the cartoon drawings do not look like it, the cytoplasm contains mostly water. Some fun facts about water and the human body:
|
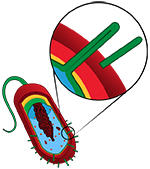 |
Bacterial pili - Long, threadlike strings coming off of the cell's surface. Bacteria can use these to bind to other bacterial cells to exchange genetic material. |
 |
Flagellum - A tail attached to the main body of a cell that can rotate to move the cell forward. Most often associated with bacterial cells. back to top |
Read more about: Building Blocks of Life
Bibliographic details:
- Article: Parts of the Cell
- Author(s): Dr. Biology
- Publisher: Arizona State University School of Life Sciences Ask A Biologist
- Site name: ASU - Ask A Biologist
- Date published:
- Date accessed:
- Link: https://askabiologist.asu.edu/cell-parts
APA Style
Dr. Biology. (). Parts of the Cell. ASU - Ask A Biologist. Retrieved from https://askabiologist.asu.edu/cell-parts
Chicago Manual of Style
Dr. Biology. "Parts of the Cell". ASU - Ask A Biologist. . https://askabiologist.asu.edu/cell-parts
Dr. Biology. "Parts of the Cell". ASU - Ask A Biologist. . ASU - Ask A Biologist, Web. https://askabiologist.asu.edu/cell-parts
MLA 2017 Style
Be Part of
Ask A Biologist
By volunteering, or simply sending us feedback on the site. Scientists, teachers, writers, illustrators, and translators are all important to the program. If you are interested in helping with the website we have a Volunteers page to get the process started.

