Illustrated by: Coleman Charters

Planet Earth is bursting with life. There are rich forests, vibrant coral reefs, and fields full of flowers in all colors of the rainbow. Animals of all shapes and sizes roam the land and water, from tardigrades to eagles, to great herds of elephants. When admiring the amazing life on our planet, have you ever wondered if we might find the same on other planets? Is Earth unique, or might space be teeming with just as many life forms?
We know that things can live in these environments on Earth, so why not on other planets? Talking of life, how did that all begin, anyway? Let’s take a look at how scientists called astrobiologists are trying to answer these questions.
Finding Habitable Planets

We know there aren’t any trees or meadows on other planets, or at least not the ones we’ve looked at yet. But then again, not all of Earth is luscious and green. We also have dry, dusty deserts and bubbling volcanoes under the sea. These are a bit more similar to some of the other places we see in our solar system.
Death Valley in the USA is one of the hottest places on Earth. It bakes under the sweltering sun and it hardly ever rains. It wouldn’t be a good place for you to live, but at the same time, you probably wouldn’t like to have a house in Antarctica, either. You want somewhere that’s just right, like Goldilocks and her porridge: not too hot, but not too cold. The same goes for planets. These are things we have to think about when we look for life. Scientists actually call the area where it’s the right temperature to survive the ‘Goldilocks Zone’.
In our own solar system, Jupiter and its gas giant neighbors Saturn, Neptune, and Uranus are too far from the sun to be warm enough. Mercury is too close and toasty. Only Venus, Earth, and Mars are in our Goldilocks Zone. We know Venus is boiling hot and full of harmful chemicals, which leaves just us and the red planet.
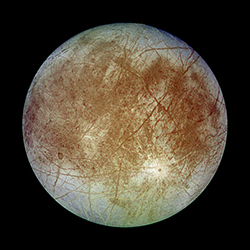
However, we may be able to add a few more places to our potential list. The moons that orbit large planets undergo a special effect called tidal heating. Huge amounts of gravity pull at these small moons so much that their rocks rub together and create friction that turns into warmth. Jupiter and Saturn have moons that might have areas that are the right temperature for life. Readings taken by spacecraft even show that a few of their moons may have liquid oceans under their icy surfaces.
Extreme Life
So now that we know where to look, how can we tell if there’s life in these places? It takes a very long time to design and build spaceships to get there and robots for collecting samples. In the meantime, astrobiologists can look at places on Earth that resemble other planets or moons. These are called analog environments.
For example, Mars is a very dry and cold planet. If we look at what survives in very cold, dry places like the Atacama desert in Chile or even Antarctica we can imagine these things could live there.
Mars also has lots of rock formations called lava flows made by volcanoes erupting a long time ago. These hold useful minerals and also make underground caves where it’s warmer than the surface. Astrobiologists use lava flows in Hawaii, Iceland, and the USA for their experiments. It’s definitely difficult to live in these places but they are far from empty. There are lots of microbes, algae, and lichen that call them home.

Another place to look on Earth are hydrothermal vents at the bottom of the ocean. We think that there are similar vents on Europa and Enceladus. Despite the water being boiling hot and full of gasses, you get plenty of microbes and even animals like worms in these places. This is exciting for astrobiologists because it means we might find life in similar habitats in space. It's also a great chance to study how these creatures are able to survive in extreme environments.
Searching for Aliens
We haven’t found evidence of life or fossils of it on other planets or moons yet, but that doesn’t mean this will never happen. Our understanding of extreme life and the tools we have to detect it have changed a lot since the first space missions. In fact, there’s a robot on Mars right now that’s looking for signs of living things and scientists from Arizona State University helped to design it. This NASA rover, called Perseverance, is collecting samples of rock to send back to Earth so they can be studied properly.

Another astrobiology mission in the making is the Europa Clipper. NASA is going to send a spacecraft to fly very close to Europa so it can map its surface and scan its ocean with radar. This craft will also have a thermal camera to show if any parts of the surface are warm from volcanic activity. Scientists can then use this information to design future missions. There are also plans to visit Titan, one of Saturn’s moons, which has lots of the chemical building blocks you need for life to be possible. The hunt for alien life is far from over, but the future is bright and full of exciting space explorations.
Additional images via Wikimedia Commons.
Read more about: Searching for Alien Life
Bibliographic details:
- Article: Searching for Alien Life
- Author(s): Finlay Warsop Thomas
- Publisher: Arizona State University School of Life Sciences Ask A Biologist
- Site name: ASU - Ask A Biologist
- Date published:
- Date accessed:
- Link: https://askabiologist.asu.edu/explore/alien-life
APA Style
Finlay Warsop Thomas. (). Searching for Alien Life. ASU - Ask A Biologist. Retrieved from https://askabiologist.asu.edu/explore/alien-life
Chicago Manual of Style
Finlay Warsop Thomas. "Searching for Alien Life". ASU - Ask A Biologist. . https://askabiologist.asu.edu/explore/alien-life
Finlay Warsop Thomas. "Searching for Alien Life". ASU - Ask A Biologist. . ASU - Ask A Biologist, Web. https://askabiologist.asu.edu/explore/alien-life
MLA 2017 Style

Earth is the right distance away from the sun for it to be not too hot or cold. There’s also lots of liquid water, which is important because every life form we know needs this to survive. What other planets exist out there that could also be the right kind of environment to support life?
Learn more about what it's like to be an Astrobiologist in the Meet Our Biologists profile, Looking For Life.
Be Part of
Ask A Biologist
By volunteering, or simply sending us feedback on the site. Scientists, teachers, writers, illustrators, and translators are all important to the program. If you are interested in helping with the website we have a Volunteers page to get the process started.

