What Plants and Foods Are GMOs?
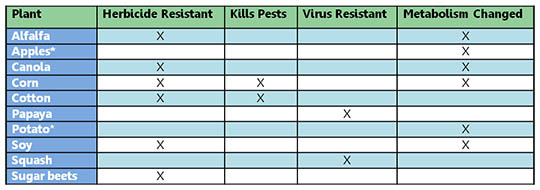
There are only a few types of transgenic, or “genetically modified,” plants that have been approved for commercial production in the United States. The table below shows those different plants and what genetic traits in the plants have been added or changed by scientists. These plants have one or more of the following traits modified by genetic engineering.

Herbicide Resistance – Herbicides are chemicals used to kill weeds. On large farms that use herbicides, these chemicals can leak into the environment or they can stick to the crops, ending up in your food in small amounts. If farmers could use less toxic chemicals to kill weeds, it would be safer for people eating the crops and for the environment. Many transgenic plants have a gene added making them resistant to a specific, low-toxicity herbicide. This allows farmers to use herbicides that do less harm to the environment and people.
Pest Resistance – Some plants have been modified to have a bacterial gene. This bacterial gene makes a protein which kills only certain types of insects that harm plants. The protein is not toxic to people or to other insects or animals, but it protects the plants from that specific pest.Because of this, farmers do not have to use toxic pesticides on these plants.
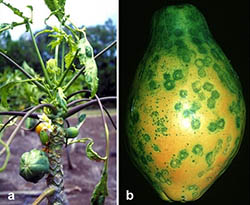
Virus Resistance – Did you know that plants can get sick from viruses? These viruses do not make people sick, but they can damage crops. Genes have been added to some plants so they won't catch these specific viruses.
Changed Metabolism – Genes have also been added to plants to change the types of sugars or fats that a plant makes. This can be used to make the plant safer to eat. Some of these genes make the plant less likely to get bruised or damaged during shipping which means less food gets thrown in the trash.
Knowing the type of genetically modified crops that we can grow, we can think more about whether growing them is safe and whether it benefits farmers.
Additional images via Wikimedia Commons. Potato image by Agricultural Research Service.
Read more about: What's a GMO?
Bibliographic details:
- Article: Which Plants Are GMOs?
- Author(s): Dr. Biology
- Publisher: Arizona State University School of Life Sciences Ask A Biologist
- Site name: ASU - Ask A Biologist
- Date published:
- Date accessed:
- Link: https://askabiologist.asu.edu/which-plants-are-transgenic
APA Style
Dr. Biology. (). Which Plants Are GMOs?. ASU - Ask A Biologist. Retrieved from https://askabiologist.asu.edu/which-plants-are-transgenic
Chicago Manual of Style
Dr. Biology. "Which Plants Are GMOs?". ASU - Ask A Biologist. . https://askabiologist.asu.edu/which-plants-are-transgenic
Dr. Biology. "Which Plants Are GMOs?". ASU - Ask A Biologist. . ASU - Ask A Biologist, Web. https://askabiologist.asu.edu/which-plants-are-transgenic
MLA 2017 Style
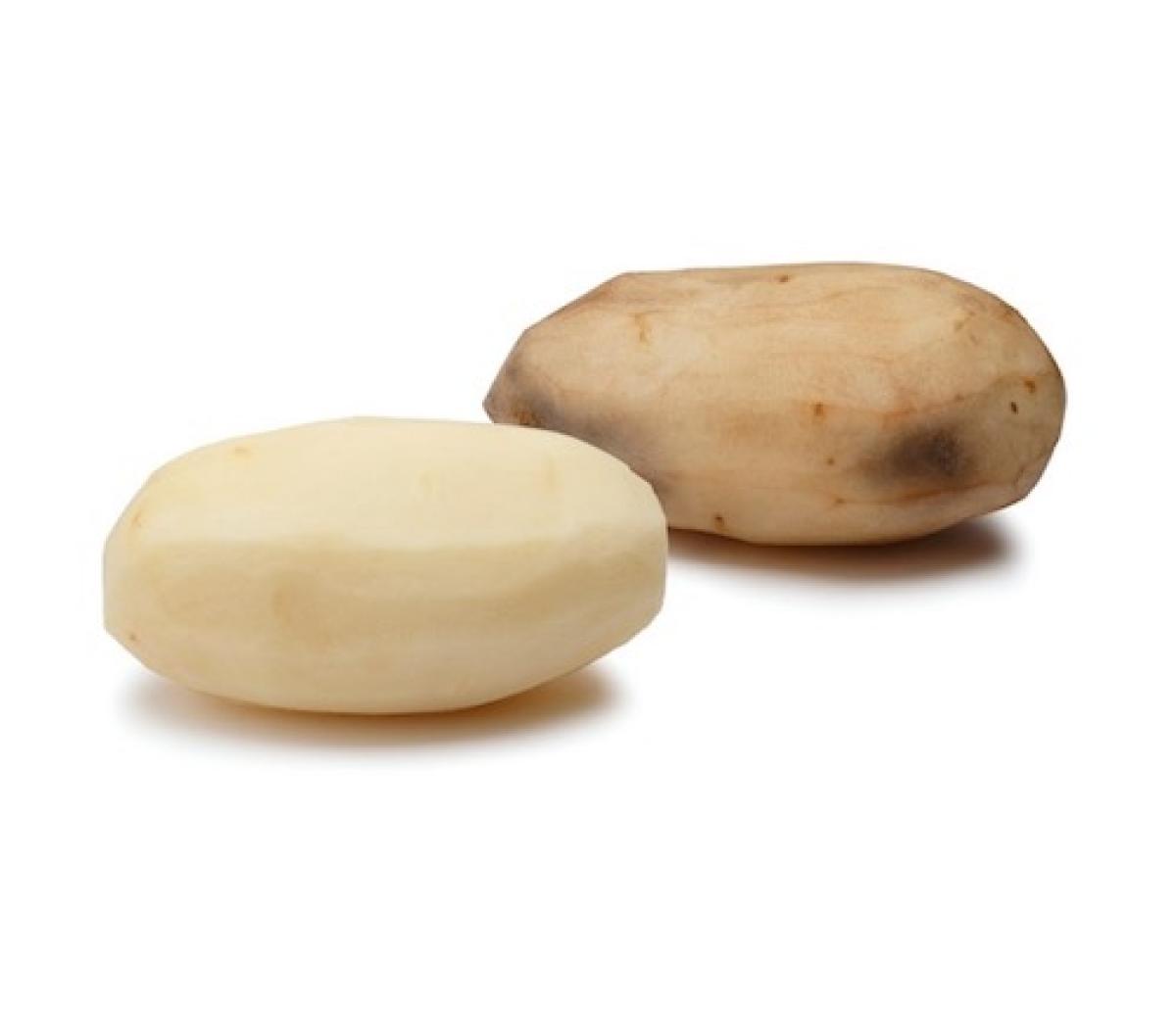

The "Innate Potato" is a type of GM potato that does not turn brown when bruised and has less sugars than non-transgenic potatoes.
Be Part of
Ask A Biologist
By volunteering, or simply sending us feedback on the site. Scientists, teachers, writers, illustrators, and translators are all important to the program. If you are interested in helping with the website we have a Volunteers page to get the process started.

